Blockchain Wallets: Choosing the best Optimal Security

Blockchain Wallets in the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency, a blockchain wallet stands as a crucial tool for anyone involved in digital finance. A blockchain wallet not only serves as a secure method for storing cryptographic keys but also plays a pivotal role in managing and then transacting digital assets. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of blockchain wallets, offering insights into their types, features, and then best practices for usage.
What is a Blockchain Wallet?
You interact with various digital tools through a blockchain wallet. Blockchain networks, enabling users to store, manage, and then Blockchain Wallets transfer cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional wallets, which handle physical currency, blockchain wallets manage digital assets through public and then private cryptographic keys. The wallet’s primary functions include:
Secure Storage: Safeguarding digital assets Blockchain
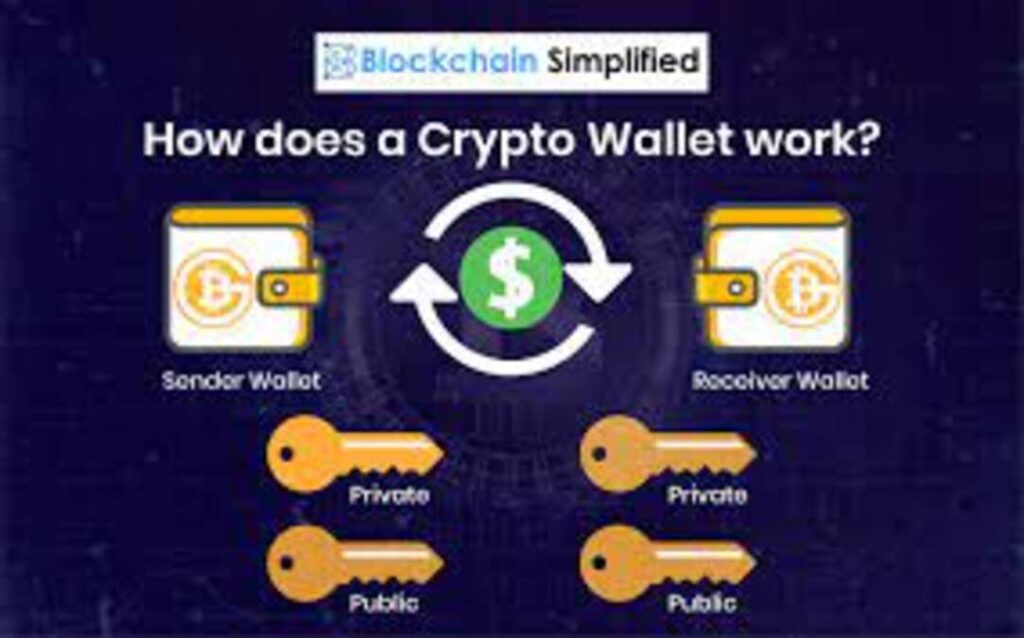
Transaction Management: Facilitating the sending and then receiving of cryptocurrencies.
Account Monitoring: Providing a detailed view of transaction history and then wallet balance.
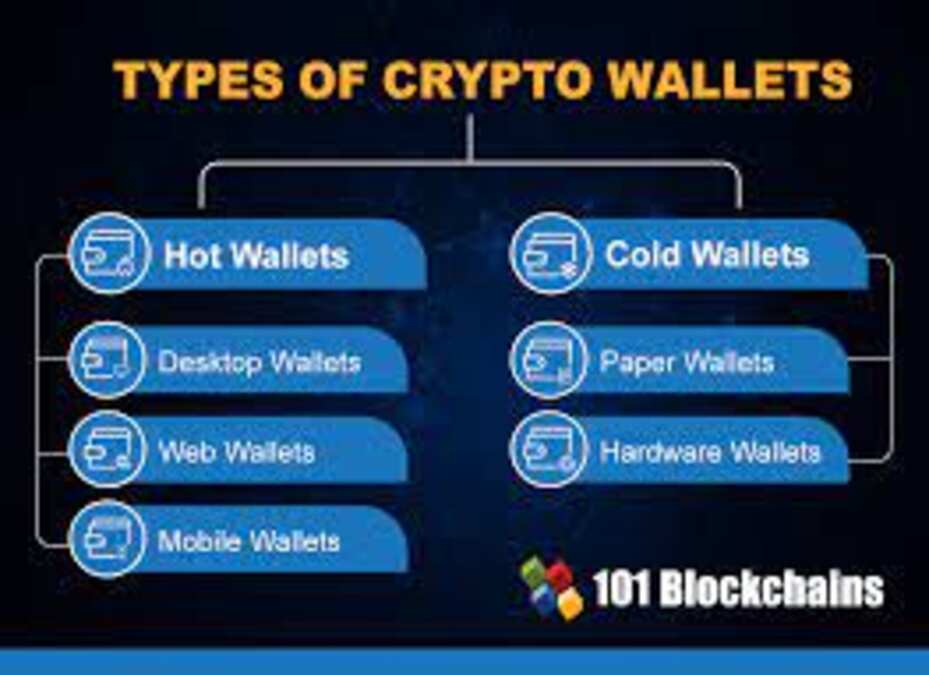
Types of Blockchain Wallets
1. Software Wallets
Software wallets are applications or programs than Blockchain Wallets users install on their computers or smartphones. These wallets are further categorized into:
a. Desktop Wallets
A personal computer is used to install desktop wallets, providing robust security features. Users have full control over their private keys and then are often chosen for their user-friendly interfaces and then extensive functionality.
Features: High security, offline storage options, advanced features.
Examples: Exodus, Electrum.
b. Mobile Wallets
Users can access their digital assets conveniently with mobile wallet apps on their smartphones. They are generally more accessible but may face security challenges compared to desktop wallets.
Features: Portability, QR code scanning, real-time notifications.
Examples: Trust Wallet, Mycelium.
c. Web Wallets
Web wallets are online platforms accessible through web browsers. They offer convenience and then easy access but come with potential security risks due to their online nature.
Features: Accessibility from any device, ease of use.
Examples: Coinbase Wallet, Blockchain.info.
2. Hardware Wallets
Users can use hardware wallets, which are physical devices, to securely store their cryptographic keys offline.
They are highly regarded for their security features, protecting users from online threats.
Features: Offline storage, physical device, enhanced security.
Examples: Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T.
3. Paper Wallets
Paper wallets involve printing out a public and then Blockchain Wallets private key on paper, which is then used to access the wallet. This method is rarely used due to its impracticality and risk of physical damage to it.
Features: Offline storage, no digital footprint.
Examples: Bitaddress.org, WalletGenerator.net.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Wallet
Selecting the appropriate blockchain wallet depends on various factors including security, convenience, and then usability. Here’s a detailed guide to help in making an informed choice:
1. Security
Security is paramount when choosing a blockchain wallet. Users should consider:
Private Key Control: Opt for Blockchain Wallets
Encryption: Ensure the wallet offers strong encryption methods.
Backup Options: Look for wallets that provide backup and then recovery options to protect against data loss.
2. Usability
The wallet’s user interface and then Blockchain Wallets ease of use can also significantly impact the user experience. Evaluate:
User Experience: Choose a wallet with a straightforward and then intuitive interface.
Support and then Updates: Ensure the wallet is regularly updated and then supported by the developers.
3. Compatibility
Verify that the wallet is appropriate for the cryptocurrency you plan to utilize. Some wallets support multiple cryptocurrencies, while others may be limited to specific ones.
4. Cost
While many wallets are free, some may involve a cost. Evaluate:
Transaction Fees: Consider the fees associated with transactions and then withdrawals.
Wallet Price: For hardware wallets, factor in the purchase price.
Setting Up a Blockchain Wallet
1. Download and Installation Blockchain Wallets
For software wallets, download the wallet from the official website or app store. For hardware wallets, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for setup.
2. Creating a Wallet
Software Wallets: Install the application, create a new wallet, and then Blockchain Wallets follow the setup instructions.
Hardware Wallets: Connect the device to your computer, install the companion software, and then set up a new wallet.
3. Securing Your Wallet
Create Strong Passwords: Use a complex password for added security.
Backup Your Wallet: Write down your recovery seed and store it in a safe then place.
4. Making Transactions Blockchain Wallets
To send or receive cryptocurrency:
Receiving: Give the sender the address from your wallet.
Sending: Enter the recipient’s address and the amount to transfer.
Best Practices for Blockchain Wallet Security
1. Regular Updates Blockchain Wallets
Update the software in your wallet to guard against security flaws.
2. Phishing Awareness
Be cautious of phishing scams. Always verify the URL of the wallet website and then avoid clicking on suspicious links.
3. Secure Backups
Store backup copies of your wallet’s recovery seed in multiple secure locations. Avoid keeping backups online.
4. Use Reputable Sources
Only download wallets from official sources to avoid malware or compromised versions.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Lost Access
Use your recovery seed to get back into your wallet if you lose access to it. Contact support if you encounter issues.
2. Transaction Delays
Transaction delays can also occur due to network congestion. Check the block chain network status and then Blockchain Wallets transaction confirmation time.
3. Security Breaches
If you suspect a security breach, immediately transfer your assets to a new wallet and contact support for further assistance.
Future Trends in Blockchain Wallet Technology
1. Integration with DeFi
Blockchain wallets are increasingly integrating with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enabling users to participate in lending, borrowing, and then yield farming.
2. Enhanced Security Features
The development of advanced security measures, such as biometric authentication and then Blockchain Wallets multi-signature support, is enhancing the protection of digital assets.
3. Cross-Chain Compatibility
Future wallets are expected to support multiple blockchain networks, providing greater flexibility and then interoperability for users Blockchain Wallets: Essential Guide to Managing Digital Assets
In the intricate world of cryptocurrency, blockchain wallets play a crucial role in the secure and then efficient management of digital assets. As the landscape of digital finance evolves, understanding the types, features, and then best practices of blockchain wallets becomes essential for optimizing your cryptocurrency experience and then safeguarding your investments. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of blockchain wallets, helping users navigate their choices and then ensure their digital assets are well-protected.
Understanding Blockchain Wallets
A blockchain wallet is a digital tool that allows users to interact with blockchain networks, manage their cryptocurrency holdings, and then conduct transactions. Unlike traditional wallets that handle physical currency, blockchain wallets use cryptographic techniques to manage digital assets. They are designed to store and then protect the user’s private keys, which are essential for accessing and then managing cryptocurrencies.
Core Functions of Blockchain Wallets
Secure Storage: Blockchain wallets securely store the private keys necessary to access and then manage cryptocurrencies. This security is vital in protecting digital assets from unauthorized access and then potential theft.
Transaction Management: Users can also send and then receive cryptocurrencies through their blockchain wallets. The wallet facilitates the transaction by signing it with the private key and then broadcasting it to the network.
Types of Blockchain Wallets
1. Software Wallets
Applications that may be installed on PCs or mobile devices are called software wallets. They come in several forms, each having advantages and then disadvantages of its own.
a. Desktop Wallets
Desktop wallets are software programs that are installed on a personal computer. They offer robust security features and then provide users with full control over their private keys.
Pros: High security, ability to operate offline, and then extensive functionality.
Cons: Vulnerable to malware and then viruses if the computer is compromised.
Examples: Exodus and then Electrum.
b. Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets are applications designed for smartphones, offering the convenience of managing cryptocurrencies on the go.
Pros: Portability, QR code scanning, and real-time notifications.
Cons: Higher risk of theft if the mobile device is lost or stolen. then
Examples: Trust Wallet and then Mycelium.
c. Web Wallets
Web wallets are online services accessible through web browsers. They provide easy access from any device but are more vulnerable to security threats.
Pros: Accessibility from any device with an internet connection and then ease of use.
Cons: Risk of hacking and phishing attacks.
Examples: Coinbase Wallet and Blockchain.info.
2. Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are tangible objects made specifically for offline private key storage. They are known for their high level of security, as they protect the keys from online threats.
Pros: Enhanced security through offline storage and physical device protection.
Cons: Higher initial cost and potential inconvenience of carrying an additional device.
Examples: Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T.
3. Paper Wallets
The public and private keys are printed out on paper in paper wallets. This method is less common due to the risks associated with physical damage and loss.
Pros: Completely offline storage and no digital footprint.
Cons: Vulnerability to physical damage and loss, less practical for frequent transactions.
Examples: Bitaddress.org and WalletGenerator.net.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Wallet
Selecting the right blockchain wallet is crucial for ensuring both convenience and security. Here are key factors to consider:
1. Security
Security should be the top priority when choosing a blockchain wallet. Look for features such as:
Control over Private Keys: Make sure you have complete command over your private keys.
Encryption: The wallet should use strong encryption methods to protect your data.
Backup and Recovery Options: Select a wallet that provides dependable backup and recovery services.
2. Usability
The wallet’s ease of use can also greatly impact your overall experience. Consider:
User Interface: A straightforward and intuitive interface will make managing your digital assets easier.
Support and Updates: Opt for wallets that are regularly updated and supported by their developers.
3. Compatibility
Verify that the wallet is compatible with the cryptocurrency you want to use. Some wallets offer multi-currency support, while others may be limited to specific digital assets.
4. Cost Blockchain Wallets
While many wallets are free, some, especially hardware wallets, may involve a cost. Consider:
Transaction Fees: Be aware of any fees associated with transactions and withdrawals.
Wallet Price: For hardware wallets, factor in the purchase price.
Setting Up and Using a Blockchain Wallet
1. Download and Installation Blockchain Wallets
For software wallets, download the application from the official website or app store. For hardware wallets, set it up according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Creating a Wallet
Software Wallets: Install the application, create a new wallet, and follow the setup instructions.
Hardware Wallets: Connect the device to your computer, install the companion software, and set up a new wallet.
3. Securing Blockchain Wallets
Create Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords to enhance security.
Backup Your Wallet: Write down your recovery seed and store it securely.
Turn on Two-Factor Authentication: If two-factor authentication is available, turn it on for increased security.
4. Making Transactions
Receiving: Share your wallet address with the sender.
Sending: Enter the recipient’s address and the amount to transfer.
Best Practices for Blockchain Wallet Security
1. Regular Updates
Update the software in your wallet to guard against security flaws and exploits.
2. Phishing Awareness
Be cautious of phishing scams. Make sure the URL is correct at all times, and stay away from dubious sites.
3. Secure Backups
Store backups of your wallet’s recovery seed in multiple secure locations. Avoid online storage.
4. Use Reputable Sources
Download wallets only from official sources to avoid malware or compromised versions.
Future Trends in Blockchain Wallet Technology
1. Integration with DeFi
Blockchain wallets are increasingly integrating with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, enabling users to participate in various financial activities such as lending and yield farming.
2. Enhanced Security Features
Advancements in security measures, including biometric authentication and then Only 24.9% of the sentences contain transition words, which is not enough. Use more of them multi-signature support, are expected to provide even greater protection for digital assets.
Read more: Duo 2FA





